6198. Minimum sum
There are two
arrays of positive integers a1..n and b1..n. Find a permutation i1, i2,
..., in of numbers 1, 2, ..., n, for which the sum
a1 * bi1
+ ... + an * bin
is minimal. Each number should
appear only once in the permutation.
Input. The first line contains the number of elements n (n
≤ 100) in the arrays. The second line contains the elements of the first
array, and the third line contains the elements of the second array. The array
elements do not exceed 106.
Output. Print the
minimal value of required sum.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
5 7 2 4 3 10 5 11 6 9 6 |
165 |
SOLUTION
greedy
Algorithm analysis
Consider the
case of arrays with two elements. Let A = {p, q} (p < q) and B = {x, y}. Let’s examine the condition under
which the sum p * x
+ q * y will be minimized. Let’s consider two permutation
options:
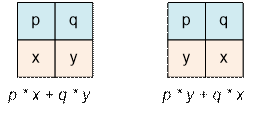
The inequality p * x + q * y < p * y +
q * x holds if
x * (p – q)
< y * (p – q)
Given that p ≠ q, dividing the
inequality by (p – q) < 0, we obtain x > y. This means that the
sum p * x + q * y (when p < q)
will be minimized if x > y.
Consider a pair
of elements from the original arrays A and B. If ai < aj and bi < bj, then by swapping bi and bj, we decrease
the total sum.
Sort array a in ascending order and array b in descending order. Then we’ll obtain the sum with the
smallest value
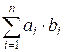
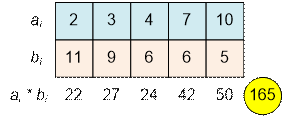
Example
Compute the sum for the
given example.
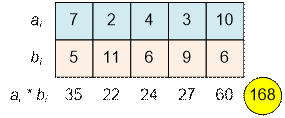
Let’s take a pair where a1 < a5 and b1 < b5. Swapping b1 and b5 will decrease the sum.
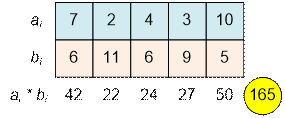
For the given
example, for any pair (i, j), if ai < aj, then bi > bj. Therefore, the current permutation is
optimal.
Let’s consider obtaining the minimum sum by sorting array a in ascending order and array b in descending order.
Algorithm realization
Declare the input arrays.
#define MAX 101
int a[MAX], b[MAX];
Read the input data.
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d",&b[i]);
Sort the first array in ascending order, and the second array in descending order.
sort(a,a+n);
sort(b,b+n,greater<int>());
Compute the desired minimum sum, which can be a 64-bit integer.
res = 0;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
res += 1LL * a[i] *
b[i];
Print the answer.
printf("%lld\n",res);
Algorithm realization – dynamic memory allocation
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
int i, n;
int *a, *b;
long long res;
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
a = new int[n];
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
b = new int[n];
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d",&b[i]);
sort(a,a+n);
sort(b,b+n,greater<int>());
for(res = i = 0; i < n; i++)
res += 1LL * a[i] *
b[i];
printf("%lld\n",res);
delete[] a;
delete[] b;
return 0;
}
Java realization
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new
Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
Integer a[] = new Integer[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
a[i] = con.nextInt();
Integer b[] = new Integer[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
b[i] = con.nextInt();
Arrays.sort(a);
Arrays.sort(b, Collections.reverseOrder());
long res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
res += 1L * a[i] * b[i];
System.out.println(res);
con.close();
}
}
Python realization
Read the input data.
n = int(input())
l1 = list(map(int,input().split()))
l2 = list(map(int,input().split()))
Sort the first array in ascending order, and the second array in descending order.
l1.sort()
l2.sort(reverse = True)
Compute the desired minimum sum.
res = 0
for i in range(n):
res += l1[i] * l2[i]
Print the answer.
print(res)